Open science is the movement to make publicly funded research publications and data accessible to all, without delay or payment.
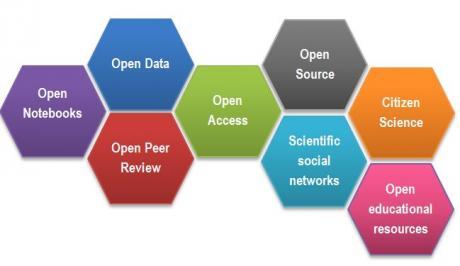
More generally, open science refers to all scientific practices that promote the sharing, transparency and reuse of research throughout its life cycle: citizen science, open research notebooks, open data, open source, open access to publications, open peer review, open educational resources, etc.
This principle of openness in research is advocated at both national and European level :
- The french Ministry of Higher Education and Innovation launched the National Plan for Open Science (2018), led by the Committee for Open Science (CoSO).
- The National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) adopted a Roadmap for open science (2019) and a Research Data plan (2020).
- As of 2019, the National Research Agency (ANR) requires all funded projects to submit the publications to an open archive, and to produce a Data Management Plan (DMP).
- The European Commission has similar requirements for projects funded under the Horizon 2020 Program.
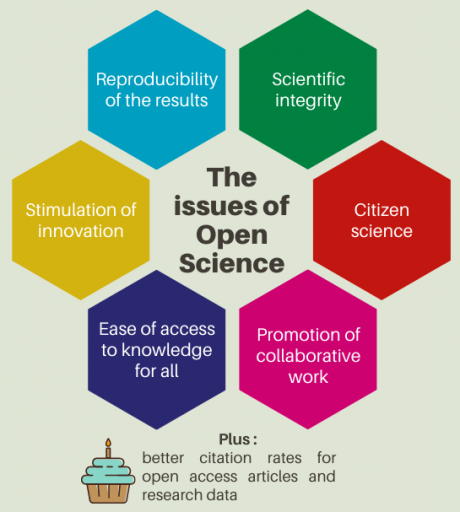
Open science aims to :
Improve the effectiveness of the research system by reducing duplication and enabling reuse of data.
Promote research integrity by offering a wider evaluation by the scientific community, enabling better reproducibility of research outcomes and early identification of scientific fraud or errors.
Strengthen citizen confidence and engagement in science.
Facilitate international collaborations to foster innovation and provide answers to contemporary societal challenges.